A complete guide to why hernias come back and how you can prevent recurrence
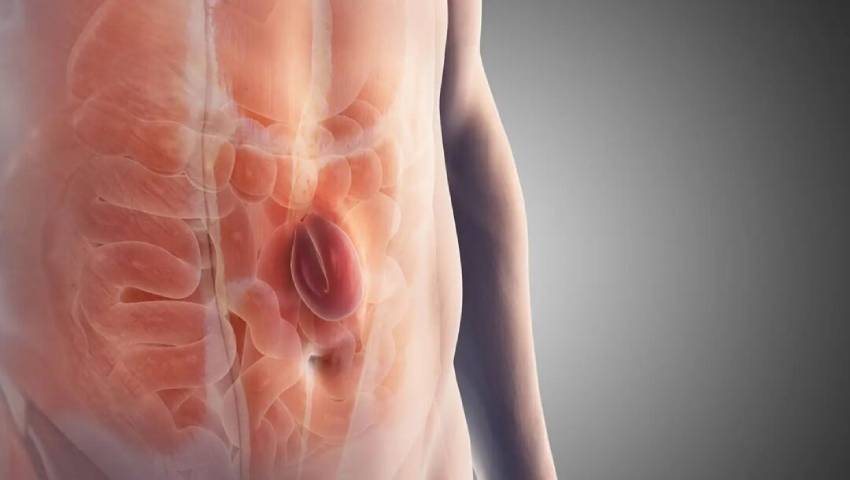
Hernia recurrence is one of the most challenging concerns for patients who have already undergone surgery. When a hernia returns at or near the previous repair site, it often becomes more complex to treat due to scar tissue, weakened abdominal muscles, and previous mesh placement. Understanding why hernias recur is the first and most important step in preventing it from happening again.
This blog explains the real reasons behind hernia recurrence, medical factors involved, lifestyle risks, and the steps you can take to protect your recovery for the long term.
Why Do Hernias Come Back?
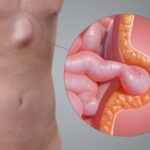
A hernia recurs when the tissue or intestine pushes again through a weak area in the abdominal wall that was previously repaired. This can happen weeks, months, or even years after the first surgery.
Below are the main causes:
1. Surgical Factors:
Sometimes recurrence happens due to issues related to the initial surgery:
- Poor repair technique or improper mesh placement
- Infection at the wound site, leading to weak scar tissue
- Poor tissue healing due to tension or trauma
- Use of unsuitable mesh or suture breakdown over time
Even a small issue during the first repair can cause weakness, making it easier for the hernia to reappear.
2. Biological Factors:
Certain people naturally have weaker connective tissues due to altered collagen metabolism.
This affects the strength of the abdominal wall and increases the chance of recurrence even after a good repair.
Conditions that weaken tissues include:
- Genetic collagen disorders
- Age-related muscle weakness
- Diabetes
- Chronic steroid or immunosuppressive medication use
3. Mechanical Stress on the Repair Site
Everyday activities can create pressure on the healing abdominal wall.
Over time, this stress can cause mesh or sutures to stretch or fail.
Common stress factors include:
- Heavy lifting too early
- Chronic coughing (smoking-related or asthma)
- Constipation and straining
- High-impact exercise during early healing
This is why surgeons emphasise strict post-surgery precautions.
Key Risk Factors for Hernia Recurrence:
You are at higher risk of recurrence if you have:
- Obesity or excess belly fat
- Smoking habit
- Chronic cough
- Constipation or urinary straining
- Poor nutrition
- Weak abdominal muscles
- Uncontrolled diabetes
Almost ALL these factors increase intra-abdominal pressure and weaken healing tissues.
Surgical Advances That Reduce Recurrence:
Thanks to modern hernia surgery, recurrence rates have dropped significantly—especially when performed by hernia specialists.
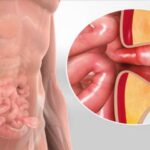
1. Synthetic Mesh Reinforcement:
Today’s repairs commonly use lightweight synthetic mesh that strengthens the weak area without causing tension.
It provides long-term support and greatly reduces recurrence.
2. Minimally Invasive Laparoscopic & Robotic Techniques
In these advanced methods:
- Smaller incisions
- Less tissue damage
- Reduced infection risk
- Less scarring
- Better placement and fixation of mesh
These directly reduce recurrence chances and speed up recovery.
3. Specialised Complex Hernia Care:
Recurrent hernias or large abdominal wall defects must be treated by specialist hernia surgeons who routinely handle complex cases.
They are trained in:
- TAR (Transversus Abdominis Release)
- eTEP
- Robotic revision surgery
- Mesh removal & re-do repair
- Abdominal wall reconstruction
Every additional recurrence makes the surgery more difficult—so choosing a specialist early improves long-term results.
How to Avoid Hernia Recurrence: Practical Steps?
- Follow Post-Operative Instructions Strictly: Avoid heavy lifting, gym activity, running, or abdominal strain during the critical healing period (at least 6–12 weeks).
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra body weight puts continuous pressure on the repair site. Losing even 5–10% weight can significantly reduce recurrence chances.
- Use Proper Lifting Techniques:
- Bend your knees
- Keep the load close to your body
- Avoid sudden twisting movements
- Strengthen Your Core (After 6–8 Weeks): Gentle exercises like pelvic tilts, modified planks, and breathing-based core activation help build natural support.
- Quit Smoking Completely: Smoking weakens collagen, slows healing, and increases chronic coughing. Smokers have up to 4 times higher recurrence rates.
- Treat Chronic Cough or Constipation Early: Straining increases pressure on the healing tissues and can break the repair.
- Keep All Follow-Up Appointments: Your surgeon needs to monitor your recovery to ensure the repair is healing properly.
Final Takeaway: Prevention Is Better Than Re-Operation
Hernia recurrence is preventable when you combine:
- Good surgical planning
- Modern mesh reinforcement
- Minimally invasive or robotic techniques
- Careful postoperative care
- Healthy lifestyle habits
Choose an experienced hernia specialist and follow disciplined post-surgery care to ensure your repair lasts a lifetime.