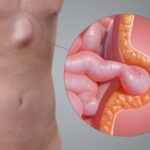
Lifestyle habits like smoking and alcohol consumption play a major role in the development, worsening, and recurrence of hernias. Many patients do not realise that these habits directly affect the abdominal muscles, connective tissues, digestion, and post-surgery healing. Whether you already have a hernia or are planning surgery, understanding these effects is extremely important for safe and long-term recovery.
How Smoking Affects Hernia Formation & Recovery?
1. Chronic Coughing → Increased Abdominal Pressure:
Smoking irritates the airways and causes chronic, persistent coughing. Every cough increases the pressure inside the abdomen, pushing the internal organs outward and worsening hernia symptoms.
This pressure is one of the most common triggers for hernia enlargement and recurrence after surgery.
2. Weakening of Abdominal Wall & Poor Tissue Strength:
Nicotine reduces blood flow to muscles and tissues.
This leads to:
- Weak connective tissue
- Poor collagen formation
- Delayed healing
Studies show smokers have almost double the risk of hernia recurrence because the abdominal wall does not regain full strength.
3. Delayed Post-Surgery Healing:
Smoking reduces oxygen supply in the blood. This leads to:
- Slow wound healing
- Higher risk of infection
- Poor mesh integration
These complications make recovery longer and more painful.
How Alcohol Consumption Worsens Hernia Problems?
1. Stomach Irritation & Acidity:
Alcohol inflames the stomach lining and increases acid reflux.
This is especially harmful for hiatal hernia patients, where acidity worsens:
- Heartburn
- Chest pain
- Regurgitation
Alcohol also triggers bloating, which increases abdominal pressure.
2. Weakening of Muscles & Connective Tissue:
Heavy alcohol intake reduces nutrient absorption and protein synthesis.
This weakens:
- Abdominal muscles
- Supporting tissues
- Surgical healing capacity
Studies show alcohol contributes to poor abdominal wall strength, raising the risk of hernia formation.
3. Dehydration & Constipation:
Alcohol dehydrates the body, leading to constipation.
Straining during bowel movements increases abdominal pressure and may worsen:
- Inguinal hernia
- Umbilical hernia
- Ventral hernia
Combined Effects of Smoking & Alcohol on Hernia Patients:
Patients who smoke and drink regularly face significantly higher risks:
Lifestyle Recommendations for Hernia Patients:
1. Quit Smoking Immediately
Stopping smoking helps:
- Reduce chronic cough
- Improve tissue healing
- Lower recurrence risk
- Enhance oxygen supply and immunity
Quitting at least 4–6 weeks before surgery improves outcomes significantly.
2. Reduce or Stop Alcohol Consumption:
Limit alcohol to protect the digestive system and reduce reflux. This prevents irritation and bloating while supporting recovery.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Obesity is a major cause of hernias.
Follow:
- High-fibre diet
- Regular walking
- Hydration
to reduce abdominal pressure and prevent constipation.
4. Consult a Hernia Specialist:
A specialist surgeon ensures:
- Proper diagnosis
- Correct surgical plan
- Pre- and post-surgery optimisation
- Lower complication risk
Personalised guidance helps prevent recurrence and long-term complications.
Key Takeaway:
Smoking and alcohol significantly worsen hernias, increase pain, delay recovery, and dramatically raise the chances of recurrence.
Quitting these habits before and after surgery improves healing, reduces complications, and ensures the best long-term results.
If you have a hernia and are a smoker or drink alcohol regularly, discuss this openly with your surgeon. Small lifestyle changes can make a massive difference in your recovery and overall health